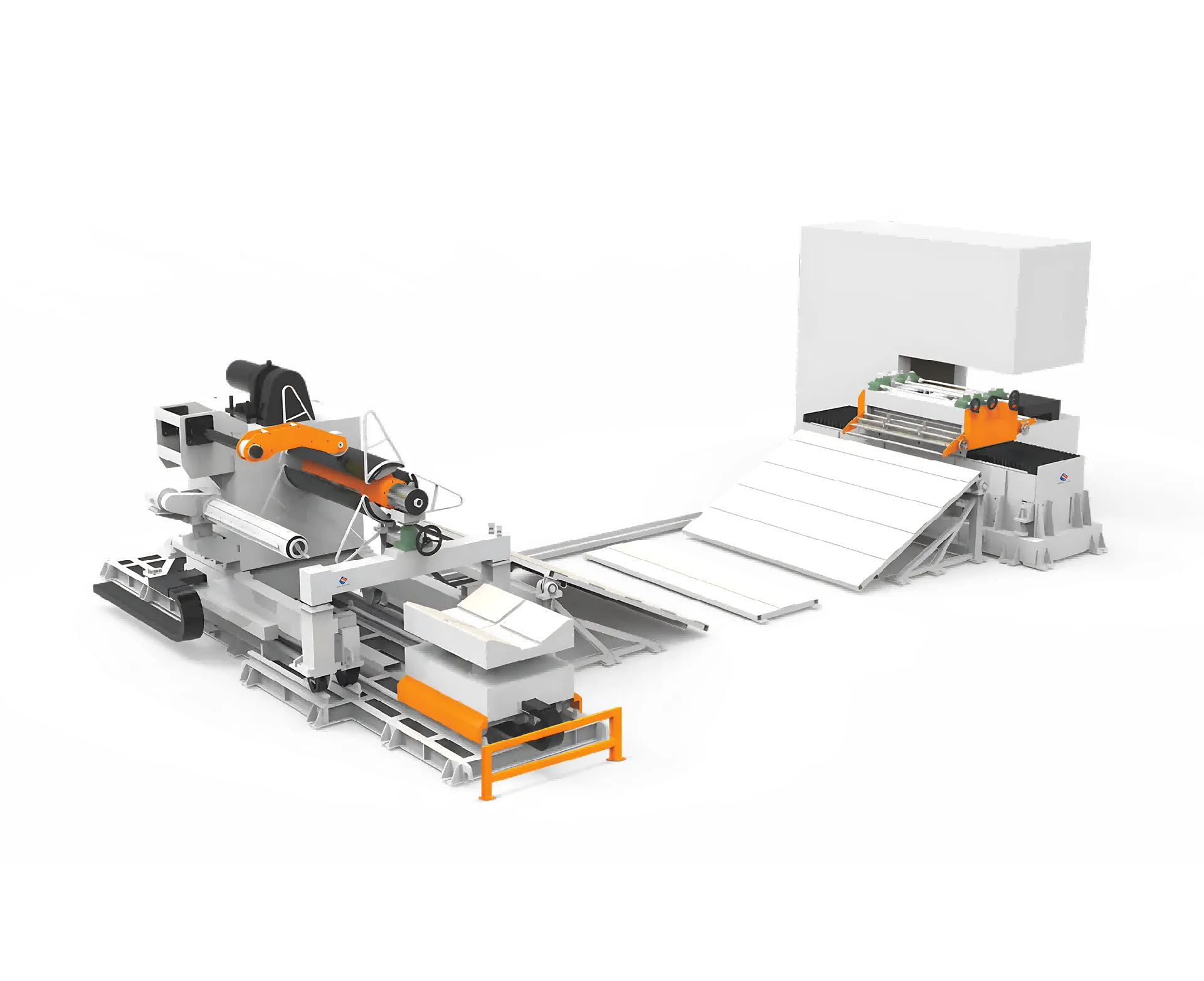
Manufacturing efficiency relies heavily on precise material handling systems that can consistently deliver components to production lines without disruption. A customized zigzag feeder represents one of the most sophisticated solutions for automated feeding applications, where precision becomes the cornerstone of operational success. These specialized conveying systems transform the way materials move through manufacturing processes, ensuring that every component reaches its destination with exact timing and positioning.
The significance of precision in feeder systems extends far beyond simple material transport. When manufacturers invest in a customized zigzag feeder, they are prioritizing accuracy that directly impacts product quality, production speed, and overall equipment effectiveness. This precision becomes particularly crucial in industries where component placement tolerances are measured in fractions of millimeters, and any deviation can result in costly production delays or quality defects.
Understanding the relationship between precision engineering and feeder performance helps manufacturers make informed decisions about their material handling investments. Modern production environments demand feeding solutions that can adapt to varying component sizes, weights, and feeding requirements while maintaining consistent accuracy throughout extended operating periods.
Engineering Fundamentals of Precision Feeding
Mechanical Design Considerations
The mechanical foundation of any customized zigzag feeder begins with precision-engineered components that work in harmony to achieve consistent feeding performance. Track geometry plays a fundamental role in determining feeding accuracy, with carefully calculated angles and surface finishes that minimize friction variations and ensure predictable component behavior. The track design must account for component characteristics such as weight distribution, surface texture, and dimensional tolerances to create optimal feeding conditions.
Vibration amplitude and frequency control systems represent another critical aspect of mechanical precision. These parameters must be precisely calibrated to match the specific requirements of different components, ensuring that feeding rates remain consistent regardless of external factors such as ambient temperature or component batch variations. Advanced feeder systems incorporate closed-loop feedback mechanisms that continuously monitor and adjust vibration characteristics to maintain optimal performance.
Material selection for feeder construction directly influences long-term precision maintenance. High-grade stainless steel tracks, precision-machined mounting surfaces, and carefully selected dampening materials contribute to dimensional stability over extended operating periods. These material choices ensure that the customized zigzag feeder maintains its calibrated performance characteristics throughout its operational lifespan.
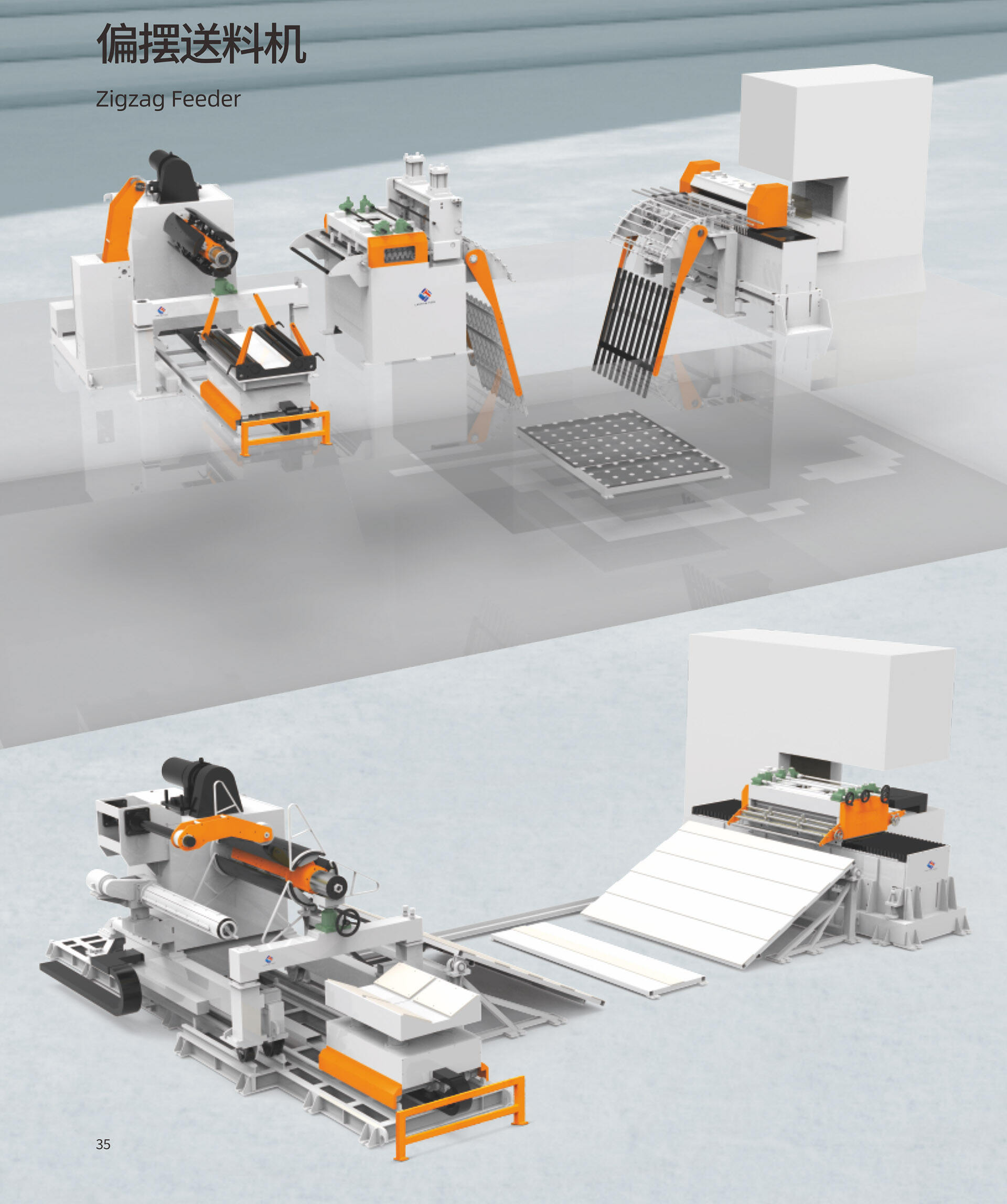
Control System Integration
Modern precision feeding systems rely on sophisticated control algorithms that monitor multiple parameters simultaneously to maintain optimal performance. Sensor integration allows real-time monitoring of component flow rates, track vibration characteristics, and feeding consistency. These sensors provide continuous feedback to control systems that can make instantaneous adjustments to maintain precise feeding parameters.
Programmable logic controllers enable customized zigzag feeder systems to adapt to different production requirements without manual intervention. These control systems store multiple feeding profiles that can be automatically selected based on component type, production speed requirements, or quality specifications. The ability to switch between feeding profiles seamlessly ensures consistent precision across diverse manufacturing applications.
Communication protocols between feeder control systems and upstream production equipment create synchronized material flow that eliminates bottlenecks and reduces waste. This integration ensures that feeding precision aligns with overall production line timing, creating smooth material flow that maximizes manufacturing efficiency.
Quality Control and Manufacturing Standards
Dimensional Accuracy Requirements
Manufacturing industries increasingly demand feeding systems that can maintain dimensional accuracy within extremely tight tolerances. A properly configured customized zigzag feeder must consistently position components within specified placement zones, typically measuring accuracy in thousandths of an inch or hundredths of millimeters. This level of precision requires careful calibration of all system parameters, from vibration amplitude to track surface conditions.
Component orientation control represents another critical aspect of dimensional accuracy in precision feeding applications. Advanced feeder designs incorporate orientation correction mechanisms that ensure components maintain proper positioning throughout the feeding process. These systems use carefully designed track features and controlled vibration patterns to guide components into correct orientations before delivery to downstream processes.
Repeatability measurements demonstrate the consistent performance capabilities of precision feeding systems. High-quality customized zigzag feeder installations typically achieve repeatability ratings better than 0.1mm across thousands of feeding cycles, ensuring that component placement remains consistent throughout extended production runs. This repeatability becomes essential in applications where downstream processes rely on precise component positioning for proper assembly or processing.
Process Validation and Certification
Comprehensive validation procedures ensure that customized zigzag feeder systems meet specified performance criteria before deployment in production environments. These validation processes include statistical analysis of feeding consistency, dimensional accuracy verification, and long-term stability testing under various operating conditions. Validation data provides manufacturers with documented evidence of system capabilities and helps identify optimal operating parameters.
Industry certification requirements often mandate specific precision standards for feeding equipment used in regulated manufacturing environments. Medical device manufacturing, pharmaceutical production, and aerospace component assembly all require documented precision capabilities that meet stringent regulatory standards. Customized feeder systems must demonstrate compliance with these standards through rigorous testing and certification processes.
Continuous monitoring and documentation systems maintain precision verification throughout the operational lifecycle of feeding equipment. These systems automatically record performance parameters and generate reports that demonstrate ongoing compliance with precision requirements. This documentation becomes essential for regulatory audits and quality management system maintenance.
Operational Benefits of Precision Engineering
Production Efficiency Optimization
Precision-engineered feeding systems directly contribute to improved production efficiency through reduced downtime and minimized material waste. When a customized zigzag feeder operates within precise parameters, it eliminates feeding irregularities that can cause downstream equipment malfunctions or require manual intervention. This reliability translates to higher overall equipment effectiveness and reduced labor costs associated with system maintenance and troubleshooting.
Consistent feeding rates enabled by precision engineering allow manufacturers to optimize production scheduling and resource allocation. Predictable material flow eliminates the need for safety buffers and reduces work-in-progress inventory levels. These improvements in material flow control contribute to leaner manufacturing operations and improved return on investment for production equipment.
Energy efficiency improvements result from precision-optimized feeding systems that eliminate unnecessary vibration and mechanical stress. Properly calibrated systems operate at optimal power levels while maintaining required performance characteristics, reducing operating costs and extending equipment lifespan. These efficiency gains become particularly significant in high-volume production environments where feeding systems operate continuously.
Quality Assurance Enhancement
Precision feeding directly impacts final product quality by ensuring consistent component placement and orientation throughout manufacturing processes. When components are delivered with precise positioning, downstream assembly or processing operations can achieve tighter tolerances and improved consistency. This enhanced quality control reduces defect rates and minimizes costly rework or scrap generation.
Traceability capabilities built into precision feeding systems enable comprehensive quality documentation throughout the manufacturing process. Advanced customized zigzag feeder systems can track individual components and record feeding parameters associated with specific production lots. This traceability becomes essential for quality investigations and regulatory compliance in industries with strict quality requirements.
Statistical process control integration allows real-time monitoring of feeding precision and immediate identification of any deviations from specified parameters. These monitoring capabilities enable proactive quality management that prevents defective products from advancing through production processes, reducing waste and improving customer satisfaction.
Industry Applications and Specifications
Automotive Manufacturing Requirements
Automotive manufacturing demands extremely precise component feeding for applications ranging from small electronic components to mechanical fasteners and precision-machined parts. A customized zigzag feeder designed for automotive applications must accommodate the high-speed production requirements typical of automotive assembly lines while maintaining precise component placement. These systems often handle components with complex geometries and varying surface finishes that require specialized track designs and feeding parameters.
Just-in-time manufacturing principles prevalent in automotive production require feeding systems that can rapidly change between different component types without sacrificing precision. Advanced feeder systems incorporate quick-change tooling and automated setup procedures that minimize changeover times while ensuring consistent feeding accuracy across different component families. This flexibility enables automotive manufacturers to respond quickly to production schedule changes and model variations.
Quality standards specific to automotive manufacturing, such as TS 16949 certification requirements, mandate documented precision capabilities and continuous improvement processes. Feeding systems must demonstrate consistent performance under statistical process control monitoring and provide comprehensive documentation of feeding accuracy and reliability metrics.
Electronics and Semiconductor Applications
Electronics manufacturing presents unique challenges for precision feeding systems due to the extremely small size and delicate nature of many components. Customized zigzag feeder systems designed for electronics applications must handle components measuring fractions of millimeters while maintaining placement accuracy that prevents damage to sensitive surfaces or electrical connections. Static electricity control becomes critical in these applications to prevent component damage and ensure consistent feeding performance.
Cleanroom compatibility requirements in semiconductor manufacturing demand specialized feeder designs that minimize particle generation and can withstand frequent cleaning procedures. These systems use specialized materials and surface treatments that maintain precision while meeting stringent cleanliness standards. Environmental controls for temperature and humidity also affect feeding precision and must be carefully managed in semiconductor applications.
High-volume production typical of electronics manufacturing requires feeding systems that maintain precision over millions of feeding cycles without degradation in performance. Wear-resistant materials and precision bearing systems ensure long-term accuracy while minimizing maintenance requirements that could disrupt production schedules.
Maintenance and Calibration Protocols
Preventive Maintenance Strategies
Maintaining precision in customized zigzag feeder systems requires comprehensive preventive maintenance programs that address all critical system components. Regular calibration checks ensure that vibration amplitude, frequency settings, and track geometry remain within specified tolerances. These calibration procedures use precision measurement equipment to verify feeding accuracy and identify any degradation in system performance before it affects production quality.
Lubrication schedules and bearing maintenance protocols prevent mechanical wear that could compromise feeding precision over time. Advanced systems incorporate automatic lubrication systems and condition monitoring sensors that track bearing performance and predict maintenance needs. This proactive approach minimizes unexpected downtime and ensures consistent feeding accuracy throughout equipment lifecycles.
Documentation and tracking systems record all maintenance activities and performance measurements, creating historical databases that enable trend analysis and predictive maintenance optimization. These records help identify patterns in system performance and guide maintenance scheduling to maximize precision while minimizing production interruptions.
Performance Monitoring and Adjustment
Continuous performance monitoring systems track key precision indicators such as feeding rate consistency, component placement accuracy, and system vibration characteristics. Real-time data collection enables immediate identification of any deviations from optimal performance parameters, allowing prompt corrective action before precision degradation affects production quality.
Automated adjustment capabilities in advanced customized zigzag feeder systems can compensate for minor variations in component characteristics or environmental conditions without manual intervention. These systems use closed-loop control algorithms that continuously optimize feeding parameters to maintain consistent precision across varying operating conditions.
Performance reporting and analysis tools provide comprehensive insights into feeding system efficiency and precision trends over time. These analytical capabilities help manufacturing engineers optimize system settings and identify opportunities for further precision improvements or efficiency gains.
FAQ
How does precision affect the overall cost of ownership for a customized zigzag feeder
Precision directly impacts total cost of ownership through reduced maintenance requirements, lower defect rates, and improved production efficiency. While precision-engineered systems may have higher initial costs, they typically deliver significant savings through reduced downtime, lower material waste, and decreased labor costs for system monitoring and adjustment. The improved reliability and consistent performance of precision systems also extend equipment lifespan and reduce replacement frequency.
What are the key precision specifications to consider when selecting a customized zigzag feeder
Critical precision specifications include dimensional accuracy tolerances, repeatability ratings, feeding rate consistency, and component orientation control capabilities. Manufacturers should also consider environmental operating ranges, vibration amplitude control precision, and the system's ability to maintain accuracy over extended operating periods. Integration capabilities with existing control systems and documentation of precision performance under various operating conditions are equally important selection criteria.
How frequently should precision calibration be performed on feeding systems
Calibration frequency depends on application requirements, production volume, and environmental conditions, but most precision feeding systems benefit from monthly accuracy verification checks and quarterly comprehensive calibrations. High-volume applications or critical manufacturing processes may require weekly verification, while less demanding applications might extend calibration intervals to every six months. Continuous monitoring systems can help optimize calibration schedules based on actual performance trends.
What factors can cause precision degradation in customized zigzag feeder systems
Common causes of precision degradation include mechanical wear in bearing systems, track surface contamination, vibration amplitude drift due to electrical component aging, and environmental changes affecting material properties. Component buildup on track surfaces, loose mounting hardware, and inadequate lubrication can also affect feeding precision. Regular maintenance and environmental controls help minimize these factors and maintain consistent system accuracy.
Table of Contents
- Engineering Fundamentals of Precision Feeding
- Quality Control and Manufacturing Standards
- Operational Benefits of Precision Engineering
- Industry Applications and Specifications
- Maintenance and Calibration Protocols
-
FAQ
- How does precision affect the overall cost of ownership for a customized zigzag feeder
- What are the key precision specifications to consider when selecting a customized zigzag feeder
- How frequently should precision calibration be performed on feeding systems
- What factors can cause precision degradation in customized zigzag feeder systems